The SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) acts as a synchronous data bus used to send data between microcontrollers and small peripherals that use separate lines for data and a clock that keeps both sides in perfect sync.
In SPI only one side generates the clock signal (SCK for serial clock). The side that generates the clock is called the Controller or the Master, and the other side is called the Peripheral or the Slave. There is always only one Controller, but there can be multiple Peripherals.
Data sharing from the Controller to the Peripheral is sent on a data line called COPI(Controller Output Peripheral Input). If the Peripheral needs to send a response back to the Controller data is sent on the line called CIPO(Controller Input Peripheral Output).
The last line is called CS (Chip select) or SS (Slave select). This tells the peripheral that it should wake up and receive/send data and is also used when multiple peripherals are present to select the one you'd like to talk to.
NOTE: Controller/peripheral is formerly known as master/slave. Arduino, ESPRESSIF, Sparkfun, etc, no longer support the use of this terminology and you probably find this in old documentation and examples of other microcontrollers. The reasons behind the terminology change can be found here. In the code examples adjoint in this project, I named the variables using the old terminology because it was the way I learned. Changes in variables using the new terminology will be reflected in the next projects.

|
| SPI Communication |
The code, files, and other details can be found and downloaded from my GitHub page.
Feel free to use the Comments section in this blog or visit my social media to learn about my job.
Introduction
The ESP32 integrates 4 SPI peripherals: SPI0, SPI1, SPI2 (HSPI), and SPI3
(VSPI).
SPI0 and SPI1 are internal and not open to users. We can use HSPI
and VSPI to communicate with other devices, and each bus can drive up to three
SPI slaves.
The examples below use VSPI with custom GPIOS, this configuration gives us the flexibility to adapt to a specific requirement (default GPIOS already used).
Below I described 3 examples using SPI communication:
Example 1 describes the simplest case where the Controller (Master) sends a message to the Peripheral (Slave) and No response back.
Example 2 describes the case where the Controller (Master) sends a message and we have a response back from the Peripheral (Slave).
Example 3 describes an application using a potentiometer in the Controller (Master) to dim an LED in the Peripheral (Slave). The idea behind this application is to use the Slave (ESP32) as an extension due to the limited GPIOS number that the Master (ESP32-CAM) has.
Prerequisites
- The project was developed using Platformio IDE and VScode. An installation tutorial can be found on the RANDOM NERD TUTORIALS blog
- The library for SPI-Controller (Master) is already included in the platform, to use the library only have to import it into your code.
- The library for SPI-Peripheral (Slave) can be found as ESP32SPISlave by hideakitai. More details and examples about this library can be found in the author's repository
- ESP32-CAM requires a USB to UART TTL converter of 5v to upload code.
Example 1: Send data from Master to Slave
Circuit Diagram
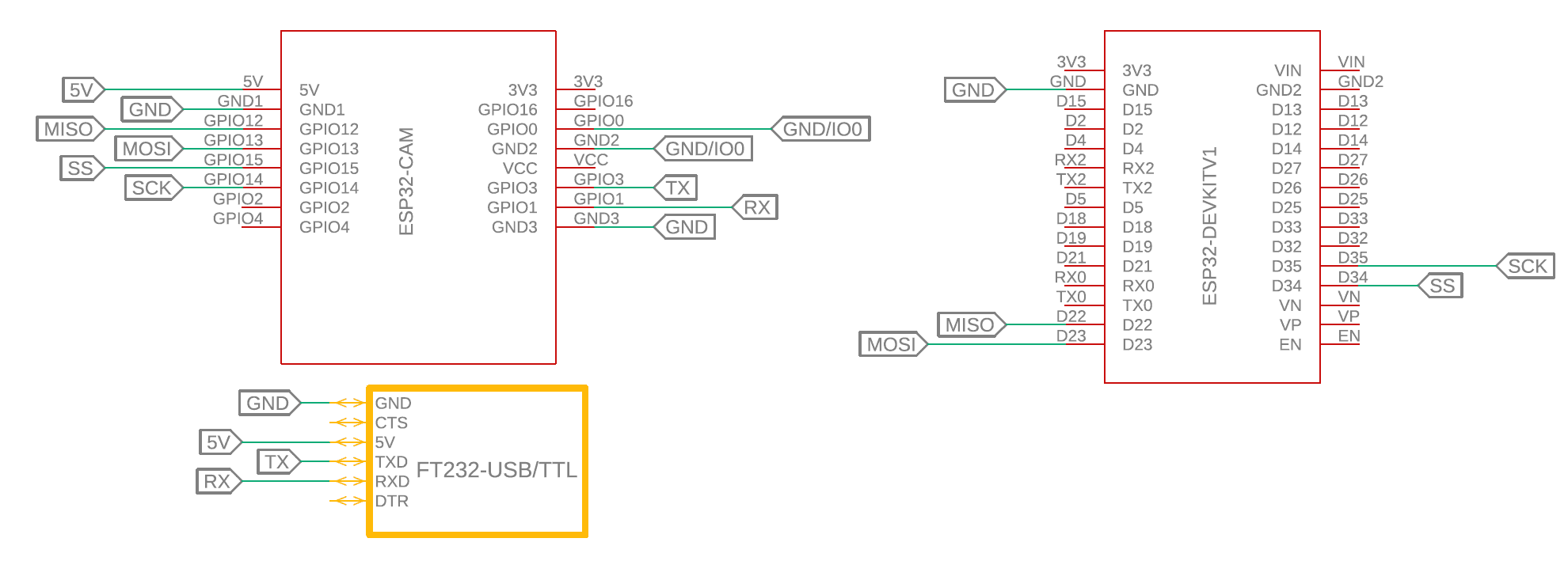
|
| Circuit diagram for Master-Slave ESP32-SPI communication |
Code
~/Master/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SPI.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 12
# define SPI_MOSI 13
# define SPI_SCK 14
# define SPI_SS 15
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
SPIClass master(VSPI);
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 12;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
/*FUNCTION DECLARATION-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String , uint8_t* , int);
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* ,int );
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
// Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as MASTER
pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS,HIGH);
master.begin(SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
// Wait for SPI to stabilize
delay(2000);
Serial.println("start spi master");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
// Message to send
String data = "Hi Slave";
strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
// Send encoded message
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(1000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW);
master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH);
master.endTransaction();
// Show encoded message
for (int i=0; i < BUFFER_SIZE;i++){
Serial.print(tx_buf[i]);
Serial.print('|');
}
Serial.println();
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*FUNCTIONS----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String data, uint8_t* buffer, int bufferSize){
/**
* Converts(encode) a String into a buffer of unsigned 8 bits integers
* input:
* - data(String): the string value
* - buffer(uint8_t): an empty pre-sized buffer
* - bufferSize(int): the size of the buffer
* output:
* - buffer(uint8_t): the filled buffer
*/
char dataBuffer[bufferSize];
data.toCharArray(dataBuffer,bufferSize+1);
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (i < data.length()){
buffer[i]=static_cast <uint8_t>(dataBuffer[i]);
}
else{
// Fill free buffer space
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>('\0');
}
}
}
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* buffer,int bufferSize){
/**
* Convert(decode) the (uint8_t)buffer into a String
* input:
* - buffer(uint8_t): buffer with unsigned 8 bits integers(0-255) values
* output:
* - result(String): decoded String
*/
String result="";
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (buffer[i]==0){
result+="";
}
else{
result+=(char)buffer[i];
}
}
return result;
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
~/Slave/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <ESP32SPISlave.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 22
# define SPI_MOSI 23
# define SPI_SCK 35
# define SPI_SS 34
// SPI settings
ESP32SPISlave slave;
// Queued transactions
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 1;
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 12;
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
/*FUNCTION DECLARATION-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String, uint8_t*, int);
String bufferToStr(uint8_t*, int);
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
//Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as SLAVE
slave.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0);
slave.setQueueSize(QUEUE_SIZE);
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
slave.begin(VSPI,SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
delay(2000);
Serial.println("start spi slave");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
// execute transaction in the background and wait for completion
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
slave.trigger();
}
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
// get the oldeest transfer result
size_t received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceived();
// decode message received
String rx_string = bufferToStr(rx_buf,received_bytes);
Serial.println(rx_string);
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*FUNCTIONS----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String data, uint8_t* buffer, int bufferSize){
/**
* Converts(encode) a String into a buffer of unsigned 8 bits integers
* input:
* - data(String): the string value
* - buffer(uint8_t): an empty pre-sized buffer
* - bufferSize(int): the size of the buffer
* output:
* - buffer(uint8_t): the filled buffer
*/
char dataBuffer[bufferSize];
data.toCharArray(dataBuffer,bufferSize+1);
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (i < data.length()){
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>(dataBuffer[i]);
}
else{
// Fill free buffer space
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>('\0');
}
}
}
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* buffer,int bufferSize){
/**
* Convert(decode) the (uint8_t)buffer into a String
* input:
* - buffer(uint8_t): buffer with unsigned 8 bits integers(0-255) values
* output:
* - result(String): decoded String
*/
String result="";
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (buffer[i]==0){
result+="";
}
else{
result+=(char)buffer[i];
}
}
return result;
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Master Code Explanation
Define custom GPIOS to use with SPI communication
# define SPI_MISO 12 # define SPI_MOSI 13 # define SPI_SCK 14 # define SPI_SS 15
Assign one of the 2 SPI available to the class Master. In this case, I used VSPI
SPIClass master(VSPI);
Define a pre-sized buffer, it must be in multiples of 4 bytes. This is where we are going to save the message we want to transmit to the Slave
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 12; uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
In the setup configuration initialize SPI as Master with custom GPIOS. The chip select pin (SPI_SS) is defined as OUTPUT in the Master and writes A HIGH value to deactivate the communication.
pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SPI_SS,HIGH); master.begin(SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
The message we want to transmit is declared as a String and with the help of a predefined function the message is encoded and saved in the buffer we created before
String data = "Hi Slave"; strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
The predefined function strToBuffer() converts a String into single values 0-255(uint8_t) and saves every value into the buffer. If the length of the message is less than the buffer length the function fills the free memory spaces with a zero value(\0) to avoid sending random values.
void strToBuffer(String data, uint8_t* buffer, int bufferSize){
char dataBuffer[bufferSize];
data.toCharArray(dataBuffer,bufferSize+1);
for (int i=0;i<bufferSize;i++){
if (i < data.length()){
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>(dataBuffer[i]);
}
else{
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>('\0');
}
}
}
To send the buffer over SPI we have to configure the SPI transaction
| SPISetting() | ||
|---|---|---|
| SPI speed | 1MHz | Maximum Slave speed transaction |
| data order | MSBFIRST | Data shifted in the most significant bit first |
| mode of transmission | SPI_MODE0 | Data Capturing on Rising |
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(1000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW); master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH); master.endTransaction();
Slave Code Explanation
Import Slave library and define custom GPIOS to use with SPI communication
#include<ESP32SPISlave.h> # define SPI_MISO 22 # define SPI_MOSI 23 # define SPI_SCK 35 # define SPI_SS 34
Define an instance of the class ESP32SPISlave in this case called "slave" (it could be any name).
ESP32SPISlave slave;
Declare the number of transactions in the queue. As we send a buffer from Master in a single transaction QUEUE_SIZE = 1.
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 1;
Define a pre-sized buffer of length equal to the Master buffer. This is where we are going to receive and save the message
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 12; uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
In the setup configuration initialize SPI as Slave with custom GPIOS. The mode of transmission has to be the same as the Master (SPI_MODE0); pass the number of transactions we declare before and configure the SPI transaction with the defined values.
slave.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0); slave.setQueueSize(QUEUE_SIZE); slave.begin(VSPI,SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
Execute transactions in the background and wait for completion
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
slave.trigger();
}
Get the oldest transfer result and decode the message using the predefined function bufferToStr(), which converts the buffer into a single String.
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
size_t received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceived();
String rx_string = bufferToStr(rx_buf,received_bytes);
Serial.println(rx_string);
}
Results

|
| Send a message to SPI-Slave |
Example 2: Send/Receive data simultaneously
Code explanation
~/Master/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SPI.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 12
# define SPI_MOSI 13
# define SPI_SCK 14
# define SPI_SS 15
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
SPIClass master(VSPI);
// VSPI clock speed
uint32_t clock_speed = 1000000;
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 16;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
/*FUNCTION DECLARATION-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String , uint8_t* , int);
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* ,int );
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
// Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as MASTER
pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS,HIGH);
master.begin(SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
// Wait for SPI to stabilize
delay(2000);
Serial.println("start spi master");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
// Message to send
String data = "Hello Slave!";
strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
// Sends an encoded message
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW);
master.transfer(tx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
//master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH);
master.endTransaction();
// Reveices an encoded message
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW);
master.transfer(rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
//master.transferBytes(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH);
master.endTransaction();
// Message received from slave
String slave_message = bufferToStr(rx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
Serial.println(slave_message);
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*FUNCTIONS----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String data, uint8_t* buffer, int bufferSize){
/**
* Converts(encode) a String into a buffer of unsigned 8 bits integers
* input:
* - data(String): the string value
* - buffer(uint8_t): an empty pre-sized buffer
* - bufferSize(int): the size of the buffer
* output:
* - buffer(uint8_t): the filled buffer
*/
char dataBuffer[bufferSize];
data.toCharArray(dataBuffer,bufferSize+1);
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (i < data.length()){
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>(dataBuffer[i]);
}
else{
// Fill free buffer space
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>('\0');
}
}
}
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* buffer,int bufferSize){
/**
* Convert(decode) the (uint8_t)buffer into a String
* input:
* - buffer(uint8_t): buffer with unsigned 8 bits integers(0-255) values
* output:
* - result(String): decoded String
*/
String result="";
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (buffer[i]==0){
result+="";
}
else{
result+=(char)buffer[i];
}
}
return result;
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
~/Slave/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <ESP32SPISlave.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 22
# define SPI_MOSI 23
# define SPI_SCK 35
# define SPI_SS 34
// SPI settings
ESP32SPISlave slave;
// Queued transactions
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 2;
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 16;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
// Custom delay
unsigned long currentTime = 0;
unsigned long previousTime = 0;
int time_ms = 5;
/*FUNCTION DECLARATION-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String, uint8_t*, int);
String bufferToStr(uint8_t*, int);
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
//Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as SLAVE
slave.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0);
slave.setQueueSize(QUEUE_SIZE);
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
slave.begin(VSPI,SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
delay(2000);
Serial.println("start spi slave");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
// Message to send
String data = "Hello Master!";
strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
// if no transaction is in flight and all results are handled, queue new transactions
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
// Receives an encoded message
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
delay(5);
// Sends an encoded message
slave.queue(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
// Trigger transaction in the background
slave.trigger();
}
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
// Get received bytes for all transactions
const std::vector<size_t> received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceivedAll();
// Message received from master
String rx_message = bufferToStr(rx_buf,received_bytes[0]);
Serial.println(rx_message);
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*FUNCTIONS----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void strToBuffer(String data, uint8_t* buffer, int bufferSize){
/**
* Converts(encode) a String into a buffer of unsigned 8 bits integers
* input:
* - data(String): the string value
* - buffer(uint8_t): an empty pre-sized buffer
* - bufferSize(int): the size of the buffer
* output:
* - buffer(uint8_t): the filled buffer
*/
char dataBuffer[bufferSize];
data.toCharArray(dataBuffer,bufferSize+1);
for (int i=0;i < bufferSize;i++){
if (i < data.length()){
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>(dataBuffer[i]);
}
else{
// Fill free buffer space
buffer[i]=static_cast<uint8_t>('\0');
}
}
}
String bufferToStr(uint8_t* buffer,int bufferSize){
/**
* Convert(decode) the (uint8_t)buffer into a String
* input:
* - buffer(uint8_t): buffer with unsigned 8 bits integers(0-255) values
* output:
* - result(String): decoded String
*/
String result="";
for (int i=0;i<bufferSize;i++){
if (buffer[i]==0){
result+="";
}
else{
result+=(char)buffer[i];
}
}
return result;
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Master Code Explanation
The code for Mater SPI is almost the same as the one shown in Example 1. With the difference this time we used 2 buffers, one buffer for sending the message to the Slave (tx_buf) and the other to receive a response (rx_buf), to avoid error communication and data lost pre-size the buffers with the same length and assign "initial values" in this case 0 to avoid random value assignment.
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 16;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
The message we want to send to the Slave is declared as String and with the help of the predefined function strToBuffer() we convert the message and save it into tx_buf buffer
String data = "Hello Slave!"; strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
In the loop now we defined 2 transactions one to send the message in buffer tx_buf and a second transaction to receive the message in buffer rx_buf
// Sends an encoded message master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW); master.transfer(tx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE); //master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH); master.endTransaction(); // Reveices an encoded message master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW); master.transfer(rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE); //master.transferBytes(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH); master.endTransaction();
Using the predefined function bufferToStr() and the received message saved in the rx_buf buffer, we show in the console the decoded message received from the Slave.
String slave_message = bufferToStr(rx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE); Serial.println(slave_message);
Slave Code Explanation
The code for Slave SPI is almost the same as shown in Example 1. With the difference this time we used 2 buffers, one buffer for sending the message to the Master (tx_buf) and the other to receive a response (rx_buf), to avoid error communication and data lost pre-size the buffers with the same length and assign "initial values" in this case 0 to avoid random value assignment.
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 16;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
This time due to we are going to send and receive a message we have 2 transactions in the queue
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 2;
The message we want to send to the Slave is declared as String and with the help of the predefined function strToBuffer() we convert the message and save it into tx_buf buffer
String data = "Hello Master!"; strToBuffer(data,tx_buf,BUFFER_SIZE);
Execute transactions in the background and wait for completion.
NOTE: A delay of 5ms is strictly required between the transactions to give them time to process buffer data. Using a delay is an easy way to send/receive data without mixing the transferring values.
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
// Receives an encoded message
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
delay(5);
// Sends an encoded message
slave.queue(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
slave.trigger();
}
Once all the transactions are completed and all results are ready, we handle the rx_buff buffer; we need only the received_bytes[0] as our first transaction in the queue receives data from the Master. With the help of the predefined function bufferToStr() converts the buffer into a String to show in the console.
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
// Get received bytes for all transactions
const std::vector received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceivedAll();
// Message received from master
String rx_message = bufferToStr(rx_buf,received_bytes[0]);
Serial.println(rx_message);
}
Results

|
| send/receive a message. NO delay included |

|
| send/receive a message. 5ms delay included |
Example 3: Dimming an LED (Slave) with a potentiometer (Master)
~/Master/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SPI.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 12
# define SPI_MOSI 13
# define SPI_SCK 14
# define SPI_SS 15
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
SPIClass master(VSPI);
// VSPI clock speed
uint32_t clock_speed = 1000000;
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 4;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
// Potentimeter
#define potPin 4
uint8_t potVal = 0;
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
// Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as MASTER
pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT);
pinMode(SPI_MOSI,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS,HIGH);
master.begin(SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
// Wait for SPI to stabilize
delay(2000);
Serial.println("start spi master");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
// Read Potentiometer values
potVal = map(analogRead(potPin),0,4095,0,255);
// Add potentiometer value to buffer
tx_buf[0] = potVal;
// Sends potentiometer value to Slave
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW);
master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH);
master.endTransaction();
// Receives Led state from Master
master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW);
master.transferBytes(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH);
master.endTransaction();
Serial.print("pot value: ");
Serial.println(potVal);
// Shows response from Slave
Serial.print("Led status: ");
switch (rx_buf[0]){
case 1:
// led off
Serial.println("OFF");
break;
case 2:
// led fading
Serial.println("FADING");
break;
case 3:
// led on
Serial.println("ON");
break;
default:
// no response
Serial.println("---");
break;
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
~/Slave/src/main.cpp
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <ESP32SPISlave.h>
// SPI custom pins
# define SPI_MISO 22
# define SPI_MOSI 23
# define SPI_SCK 35
# define SPI_SS 34
// SPI settings
ESP32SPISlave slave;
// Queued transactions
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 2;
// Buffer size must be multiples of 4 bytes
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 4;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
// Led
# define LED 27
uint8_t led_channel = 1; // PWM channel (16 channels available)
uint8_t led_resolution = 8; // 8-bit resolution (0-255)
uint32_t led_freq = 1200; // PWM frecuency
/*VOID SETUP CONFIGURATION-------------------------------------------------------*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Driving led with PWM
pinMode(LED,OUTPUT);
ledcSetup(led_channel,led_freq,led_resolution); // Initialize PWM
ledcAttachPin(LED,led_channel); // Assign LED(GPIO) to channel 1
delay(2000);
//Initialize SPI bus with defined pins as SLAVE
pinMode(SPI_MISO,OUTPUT);
slave.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0);
slave.setQueueSize(QUEUE_SIZE);
// VSPI or HSPI (virtual or hardward SPI)
slave.begin(VSPI,SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
Serial.println("start spi slave");
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*LOOP---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void loop(){
// if no transaction is in flight and all results are handled, queue new transactions
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
// Receives potentiometer values from Slave
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
// Sends Led status to Master
delay(5);
slave.queue(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
// Trigger transaction in the background
slave.trigger();
}
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
// Get received bytes for all transactions
const std::vector<size_t> received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceivedAll();
//size_t received_bytes = slave.numBytesReceived();
// Message received from master
ledcWrite(1,rx_buf[0]); // Control PWM on channel 1
// Shows the buffer
for (int i=0; i<received_bytes[0];i++){
Serial.print(rx_buf[i]);
Serial.print('|');
}
Serial.println();
// Attach response
switch (rx_buf[0]){
case 0:
// led off
tx_buf[0] = 1;
break;
case 255:
// led on
tx_buf[0] = 3;
break;
default:
// led fading
tx_buf[0] = 2;
break;
}
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Master Code Explanation
Define custom GPIOS to use with SPI communication
# define SPI_MISO 12 # define SPI_MOSI 13 # define SPI_SCK 14 # define SPI_SS 15
Assign one of the 2 SPI available to the class Master. In this case, I used VSPI
SPIClass master(VSPI);
Declare SPI speed clock at 1MHz (1000000Hz), the maximum clock speed for SPI communication with an ESP32 board as SPI-Slave
uint32_t clock_speed = 1000000;
Define the pre-sized buffers, it must be in multiples of 4 bytes. This is where we are going to receive/send the message from/to the Slave. To avoid error communication and data loss assign "initial values", in this case 0, to avoid random value assignment in data transmission
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 4;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
Connect a potentiometer to GPIO 4, and define the variable potVal to save the read potentiometer values
#define potPin 4 uint8_t potVal = 0;
In the setup configuration initialize SPI as Master with custom GPIOS. The chip select pin (SPI_SS) is defined as OUTPUT in the Master and writes a HIGH value to deactivate the communication.
pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT); pinMode(SPI_SS,OUTPUT); pinMode(SPI_MOSI,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(SPI_SS,HIGH); master.begin(SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
Default reading values from a potentiometer using an ESP32 are integer values in the range 0 - 4096, and to keep things simple we have to escalate those values to an 8-bit representation, integers in the range 0-255 easily transferable in the buffer.
potVal = map(analogRead(potPin),0,4095,0,255); tx_buf[0] = potVal;
In the loop now we define 2 transactions one to send the scaled potentiometer values in buffer tx_buf and a second transaction to receive the LED state in buffer rx_buf
// Sends potentiometer value to Slave master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW); master.transferBytes(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH); master.endTransaction(); // Receives Led state from Master master.beginTransaction(SPISettings(clock_speed, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0)); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, LOW); master.transferBytes(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE); digitalWrite(SPI_SS, HIGH); master.endTransaction();
Interpret the Led state values received and show them in the console
Serial.print("Led status: ");
switch (rx_buf[0]){
case 1:
// led off
Serial.println("OFF");
break;
case 2:
// led fading
Serial.println("FADING");
break;
case 3:
// led on
Serial.println("ON");
break;
default:
// no response
Serial.println("---");
break;
}
Slave Code Explanation
Import ESP32SPISlave.h library and define custom GPIOS to use with SPI communication
#include<ESP32SPISlave.h> # define SPI_MISO 22 # define SPI_MOSI 23 # define SPI_SCK 35 # define SPI_SS 34
Define an instance of the class ESP32SPISlave in this case called "slave" (it could be any name).
ESP32SPISlave slave;
Due to we are going to receive/send a message we have 2 transactions in the queue
static constexpr size_t QUEUE_SIZE = 2;
Define a pre-sized buffer of length equal to the Master buffer. This is where we are going to receive/send the message
static constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 4;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUFFER_SIZE]{0,0,0,0};
To control an LED with a PWM signal with an ESP32 we have to add a PWM channel from the 16 available, configure the bit resolution of data (8-bit can handle values in the range 0-255), and the frequency of the PWM as1200Hz
# define LED 27 uint8_t led_channel = 1; uint8_t led_resolution = 8; uint32_t led_freq = 1200;
In the setup configuration initialize SPI as the Slave with custom GPIOS. The mode of transmission has to be the same as we declared in the Master (SPI_MODE0), pass the number of transactions we declared before, and configure the SPI transaction with the defined values.
pinMode(SPI_MISO,OUTPUT); slave.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0); slave.setQueueSize(QUEUE_SIZE); slave.begin(VSPI,SPI_SCK,SPI_MISO,SPI_MOSI,SPI_SS);
Execute transactions in the background and wait for completion.
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsHandled()) {
// Receives potentiometer values from Slave
slave.queue(NULL, rx_buf, BUFFER_SIZE);
// Sends Led status to Master
delay(5);
slave.queue(tx_buf, NULL, BUFFER_SIZE);
// Trigger transaction in the background
slave.trigger();
}
Once all the transactions are completed and all results are ready, we handle the rx_buf buffer
if (slave.hasTransactionsCompletedAndAllResultsReady(QUEUE_SIZE)) {
...
}
Save the bytes for all the transactions
const std::vectorreceived_bytes = slave.numBytesReceivedAll();
To generate the PWM signal into the LED, Write the received value from the Master in the chosen PWM channel
ledcWrite(1,rx_buf[0]);
Shows the entire buffer
for (int i=0; i<received_bytes[0];i++){
Serial.print(rx_buf[i]);
Serial.print('|');
}
Save the LED state into the tx_buf buffer to send to the Master
switch (rx_buf[0]){
case 0:
// led off
tx_buf[0] = 1;
break;
case 255:
// led on
tx_buf[0] = 3;
break;
default:
// led fading
tx_buf[0] = 2;
break;
}


Comments
Post a Comment